Physiotherapy after stroke
Physiotherapist plays a very important role in achieving the success of stroke rehabilitation and recovery. Physiotherapy is very important in acute stroke care as well as in stroke rehabilitation. In order to maximize the chance of stroke recovery as well as to reduce lethal stroke related complications e.g. pneumonia, deep vein thrombosis and decubitus ulcers etc, physiotherapy should be started immediately after a stroke; even for patients suffering from severe stroke with gross disability or remaining unconscious

Physiotherapy helps in assisting drainage of bronchial secretion and thus minimize sputum retention, so as to preventing lethal pneumonia. Weeks after a stroke, the muscle tone of the paralysed limbs may be building up to form spastic muscle. Immobilized stroke patients are thus have high risk of developing deep venous thrombosis (DVT) as lethal stroke complication. Pressure stockings and regular muscle massage or limbs stretching help in preventing DVT. For some high-risk patients, oral anti-coagulant drug may be required for DVT prophylaxis.
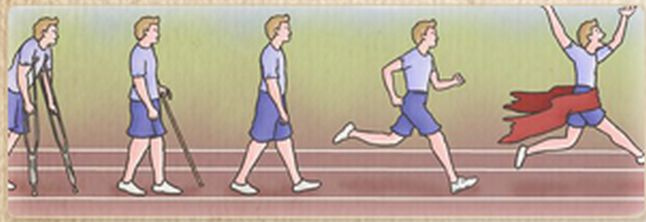
In order to treat muscle spasticity and to prevent permanent joint stiffness, physiotherapist may regularly stretch the limbs of stroke patients within their normal joints ranges. Physiotherapist will also assess the stroke patient according to the severity of stroke, the affected parts of the body, the lifestyle patterns of the patients and the progress of the initial stroke rehabilitation. Targets and goals of the stroke rehabilitation will then be set. To allow patients for easy practicing and to skill every movement, walking motions are broken down into a few simple actions, stroke patients may relearn walking as a child does.
Stroke physiotherapy starts at bedside, begins with pulling the paralysed muscle and passively stretching the paralysed limbs. This helps to reduce muscle spasticity and joints stiffness. Later on, physiotherapist will guide the patients for body balancing during sitting up and standing up, and teach them how to move back and forth between bed and chair. The next step will be teaching patient how to stand, how to use aids, how to shift their weight from one leg to the other leg. Once physical therapy rehabilitation program begun, intensive treatment schedule will follow. During the initial stages, patients may feel difficult, frustrated, tired and fatigue; however, these movements are essential for long-term stroke rehabilitation. Thus supports and encouragements from medical staffs, relatives and friends are very important to the disabling stroke survivors. Besides, adequate rest and good quality of sleeping at night is also crucial for brain cells recovery.
At last, stroke rehabilitation physiotherapy will not end after hospital discharge. On the contrary, patients should regularly attend physical therapy at hospital, clinic or home for ongoing stroke rehabilitation in order to achieve a sustainable and complete recovery of their impaired neurological functions.