The Hong Kong Minimally Invasive Brain & Spine Neurosurgery Centre has top specialists who treat complex neurological conditions caused by stroke, tumors, hernias, injuries, and traumas. Each day our skilled neurosurgeons perform dozens of complicated surgeries, saving people’s lives and helping them to restore their health. Thousands of patients go through the doors of our neurosurgery center every year which gives our excellent team of surgeons unparalleled expertise and ability to guarantee exceptional results to all of the patients.
If you are looking for an excellent neurosurgery clinic in Hong Kong, you have come to the right place. Fill in the online form to make an appointment with one of our specialist and start your journey to a healthy and happy life!
Initial stage of treatment is drug therapy for one or two months. The effectiveness of drugs in controlling the pain can help clinical diagnosis. But medications can only be a temporary solution, not a permanent cure for the true cause of trigeminal neuralgia that is: external factors compressing on the nerve and make it short-circuit.
Brain tumors can be subdivided into non-cancerous benign tumor and malignant cancerous tumor. If a tumor is originated within brain compartment ......
Tumors can develop in the vertebrae, nerves, and other tissue throughout your spine. Some spine tumors, such as astrocytomas, occur more commonly in children and adolescents......
Given the disease burden of strokes, prevention is an important public health concern. As stroke neurosurgeons, we do not want to treat stroke unless we are forced to do so for acute stroke ......
Brain tumors grow and compress normal brain tissue. Both benign and malignant tumors can cause swelling of the brain and raised intracranial pressure. Headache, dizziness....
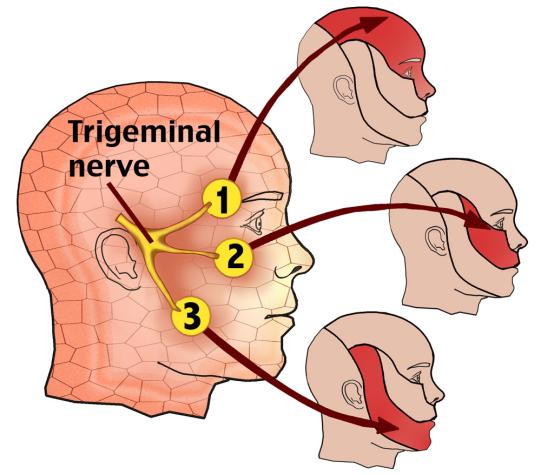
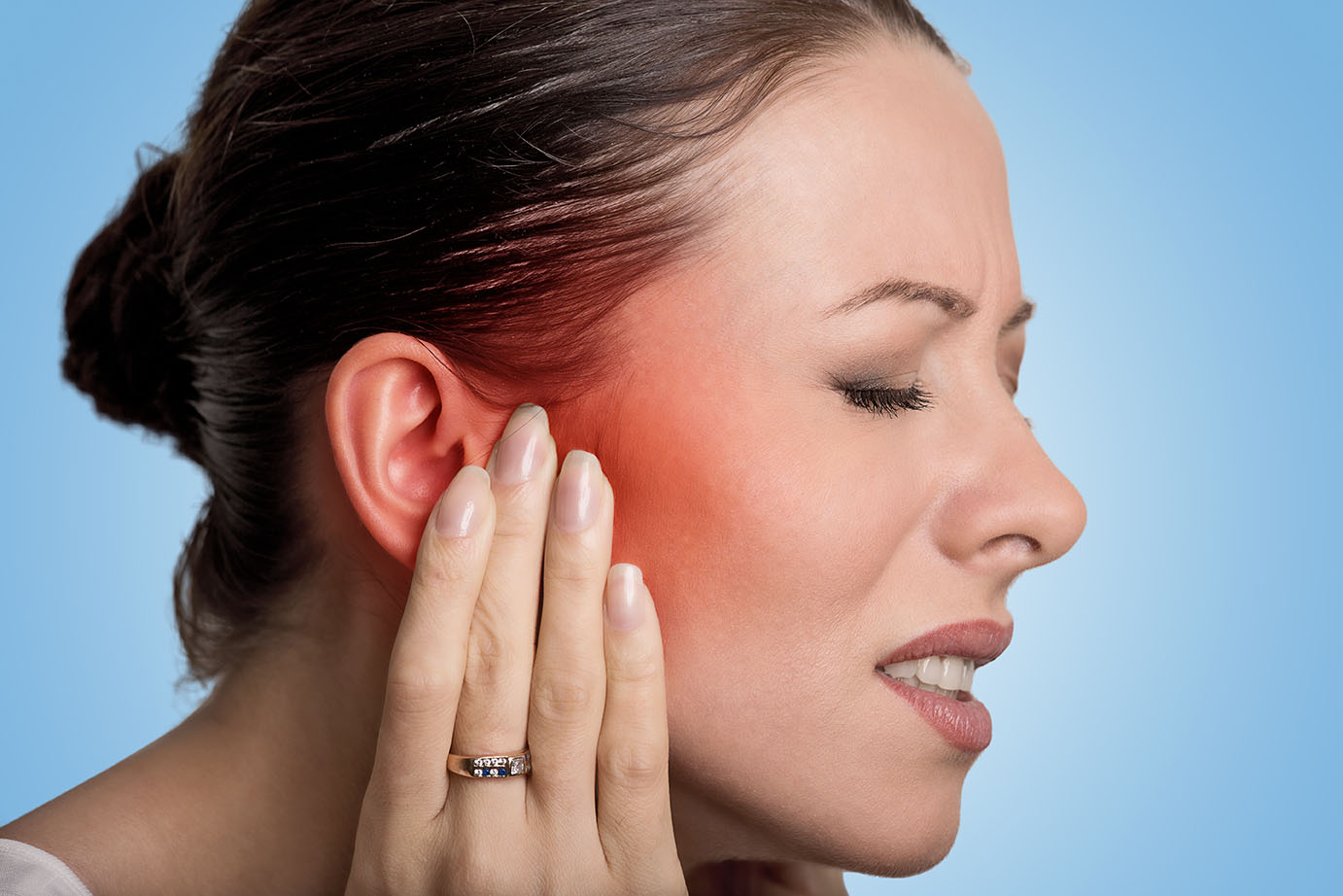
Trigeminal nerve is the 5th pair of cranial nerve at our brain. It contains mixed type of nerve fibers: general somatic sensory, visceral sensory fibers and motor fibers for muscle of mastication.
Trigeminal nerve thus controls the feeling of our face, mouth, nose and it also controls the movement of our masticatory muscle.
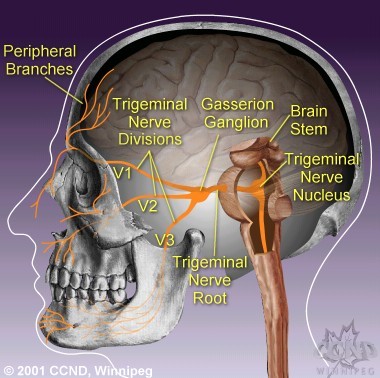
Trigeminal nerve sub-divides into the first Ophthalmic branch for the forehead region, the second maxillary branch for the cheek region and the third mandibular branch for the jaw region.
 |
 |
Primary:
Secondary:
Risk factors of developing primary trigeminal neuralgia
No indication or warning:
Sharp attack of pain, without any warning, usually at one side
Triggered by certain movements or the external factors: air flow, chewing, temperature changes, etc.
Short but intense:
Patients often describe the pain as burning, electric shock, needles, or stabbed by a knife, some cases may accompanied by other symptoms when pain appears:
e.g. facial muscle twitching, tearing, drooping of saliva, facial flushing, and conjunctival congestion, etc.
May be more serious:
As the disease progresses and worsens, disease-free intervals will be getting shorter and attacks become more frequent.
Characteristics of trigeminal neuralgia
Common trigger points:
Though diagnosis for neuropathic pain is not difficult, but there are often misdiagnoses.
We mainly rely on clinical judgment, but sometimes X ray, CT scan and MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) do help in diagnosis.
In addition, doctors must exclude the possibility of tumors, such as Acoustic neuromas, Cholesteatoma, Hemangioma, Meningioma or Epidermoid cyst, etc.
Brain tumors grow and compress normal brain tissue. Both benign and malignant tumors can cause swelling of the brain and raised intracranial pressure. Headache, dizziness, visual blurring and epileptic seizure are the common presentating symptoms of brain tumour. Other symptoms vary and mainly depend on the location of tumor at different region of the brain to affect different brain functions.
Method of treating brain tumors include: steroids, anit-convulsants, surgery, radiation therapy and chemotherapy.
Treatments can be single or combination of the above.
Prompt and early treatment
Prompt and early treatment of brain tumour can prevent or reduce neurological deficits. For example, steroid therapy to treat brain swelling and anti-convulsive medication to treat or prevent epileptic seizures.
Steroid therapy
Steroid can remove swelling or extra brain fluid of adjacent normal brain tissue around the tumour. It will make patients feel more comfortable and lead to dramatic symptomatic improvement. Steroid is usually used before, during and after surgery and radiotherapy.
Definite treatment
Choice of definite treatment for brain tumour depends on:
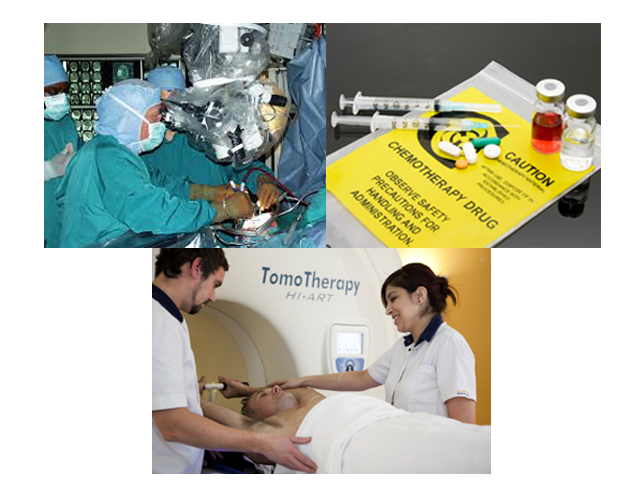
Surgery
Most benign brain tumor can be completely removed by surgery. For brain cancer, neurosurgeon may decide to remove part of the tumor in order to reduce the pressure on normal brain, so to improve patient's symptoms.
Brain tumor surgery, normal involve opening of skull bone, i.e. also known as craniotomy。 The surgery require general anesthesia, and usually require hair shaving. The aim of the surgery is to remove the tumor while preserving normal brain tissue and its vessels, so as to preserve normal brain function.
Highly malignant brain tumor - malignant glioma or Glial Blastoma Multiforme ( GBM) is well known brain cancer. Brain cancer, despite its invasive nature to surrounding brain, usually do no spread to other organs of the body i.e bone, lung or liver. However it will spread out finger-like extensions in all directions to invade surrounding important brain tissues such as motor area of the brain, brain stem, or even cross the midline to the opposite side of the brain. The invasion cause complete surgery tumor resection very difficult, and with considerable risks leading to serious neurological complications. In that instance, for patient safety and to preserve patient's intact neurological function, limited tumor resection to reduce intracranial pressure inside head, later supplemented by radiotherapy or chemotherapy is the best treatment option. Brain cancer cells may also spread to spine via cerebrospinal fluid.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy is the use of high-energy radiation to destroy cancer cells, making them unable to breed, while minimising the damages to surrounding healthy brain cells.
Brain cancer, after surgery, usually require whole brain radiation therapy. Radiotherapy is to be performed on daily basis over 4 weeks duration. Target chemotherapy may be given at the same time of radiation therapy to enhance treatment efficacy.
Radiosurgery ( i.e. Cyberknife, Gamma-knife, or X-knife ) is a kind of focal radiation treatment to small volume of tissue target i.e. tumour cells only. Its main application is for small benign tumour of less than 3 cm in size e.g. acoustic neuroma or inoperable deep seated benign tumor i.e. meningioma, etc.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy drugs kill cancer cells by disrupting the cycle of cancer cells growth and cell division. Sometimes it is used alone or combine with radiation therapy. Chemotherapy for brain tumors is usually given as outpatient basis.
Stroke sometimes referred as a cerebrovascular accident CVA), is a disease that affects the blood vessels at neck or brain, causing disturbance of blood supply to brain or causing pressure to brain, leading to the rapid loss of brain function. 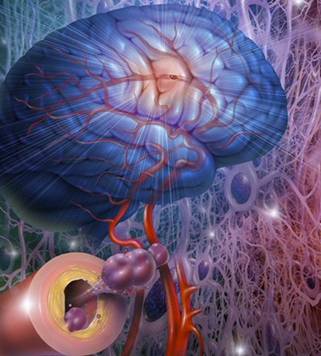
Effects of stroke:
The brain is an extremely complex organ that controls various body functions. If a stroke occurs, brain cells and body functions may be permanently damaged, it may even cause death.
Urgency of Stroke:
A stroke is a medical emergency, require urgent treatments in order to minimize the chance of permanent neurological damage and death.
How common is stroke?
Stroke is the 4th leading cause of death in Hong Kong. There were around 25000 stroke cases happened every year, around 68 stroke cases happened every day.
How stroke be compared with heart attack?
Heart attack is more common than brain attack, ranked the second killer in Hong Kong. Both heart attack and brain attack (stroke) are due to vascular disease of various causes. Patients suffering from either one of them have similar chance of being death. However survivors of heart attack can enjoy normal life without any physical disability, most of the stroke survivors however are permanently handicapped. Thus stroke is leading to a tremendous impact to patients themselves, their family, their social life and the whole society.
Physical Impact of stroke:
Depend on the type and the severity of stroke, among all stroke patients, stroke caused death in 25%-60% of them and caused permanent disability in 75-90% of them. Therefore disabling stroke survivors is the leading cause of disability in our community.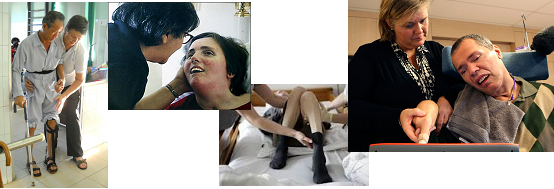
Family impact of stroke:
Stroke not only disable a patient, but it also disable patient’s whole family (spouse, parents, offspring and other relatives). To take care a stroke patient, the whole family exhaust their efforts in term of physical supports, psychological supports, financial expenditure and loss, and disturbance of their normal social life. Stroke not only disrupt the long term family planning i.e. offspring’s education, but also the harmony of the whole family.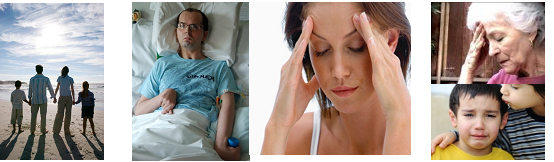
Psychological impact of stroke:
Depression and suicidal tendency are common among stroke survivors and their relatives.
Financial impact of stroke:
Not only the stroke patient loss his regular salary income for a long period or for life, but also his or her spouse or parents who take care the patient. In addition to the medical expenditures required for stroke care and rehabilitation, the whole family faces a huge financial burden.

Impact of stroke to our community:
Stroke causes huge financial cost to our community and Government. Not only the direct cost involving in the medical care for stroke patients is huge (acute phase, rehabilitation phase and infirmary phase), but also the indirect cost. The indirect cost involves the loss of productivity of the patients themselves and that of their care-takers, also involves the indirect economic loss due to familial and social harmony.
Decades ago, diagnosing and treating brain tumors were with great difficulties. With advancing imaging and microsurgical techniques, many brain tumors can be nowadays diagnosed at an early time, so as to increase the cure rate for treating brain cancer.
Brain tumors can be subdivided into non-cancerous benign tumor and malignant cancerous tumor.
If a tumor is originated within brain compartment, it is called primary brain tumor. If a tumor was spread from other parts of the body and go to the brain, it is called secondary brain tumor. Some types of cancer, i.e. lung cancer and breast cancer are more likely to spread to the brain.
As long as those benign brain tumors can be treated by surgery in time, they generally do not pose a threat to life. Though sometimes tumor cells remain after surgery may grow again, this type of recurrent benign tumors can again be surgically removed. If benign brain tumors grows at inappropriate locations or if they are big in size, they may be life-threatening. For malignant brain tumor, though rarely spread to other parts of the body, they may penetrate into the surrounding normal brain tissue and pose a threat to life.
There are more than 40 types of brain tumor, can be grossly divided into two main categories, namely benign and malignant tumors.
Benign tumor
Malignant tumors
Hydrocephalus
Brain fluid (cerebrospinal fluid) is contained within brain cavities and flow through narrow corridor at some regions. If brain tumor blocks the flow of brain fluid, there will be increase in hydraulic pressure and will put pressure on the brain; may resulting in cerebral edema or brain swelling.
What cause of brain cancer is still remains unclear. However, the following factors may contribute:
However many patients were without any of the above listed risk factors.
Staging for brain tumor
Brain tumors are categorized into four stages depending on their rate of growth as well as their ability to invade nearby tissue.
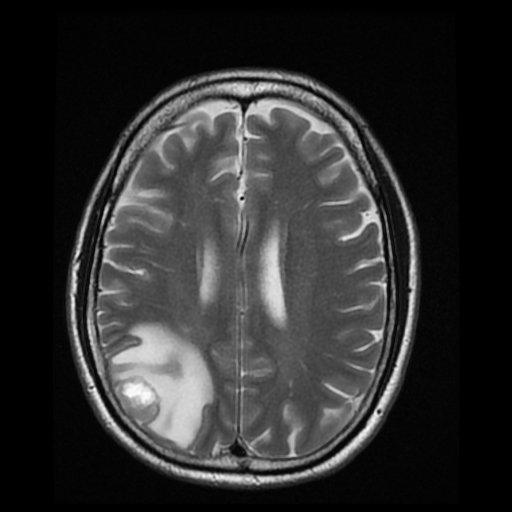
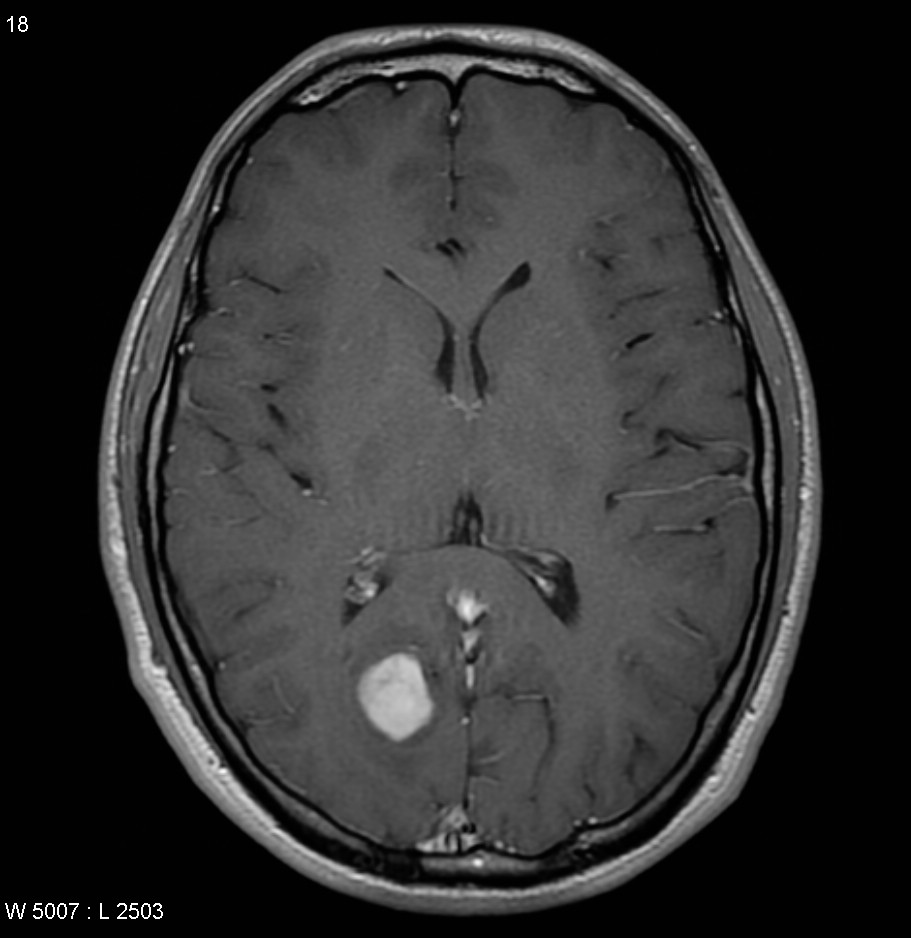
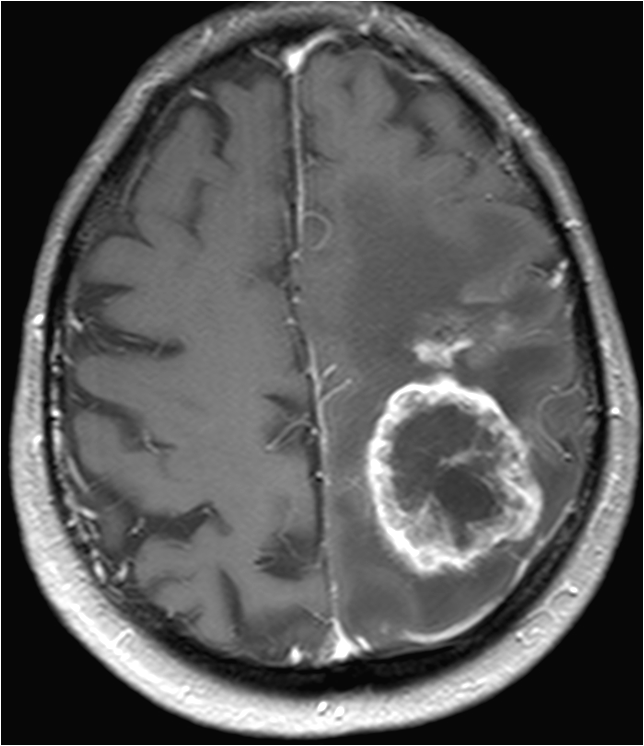
Patients with brain tumors may complain symptoms of headache, dizziness, vomiting, blurred vision, limbs weakness, etc.. Other symptoms include seizures and endocrine disorders; Personality or behavior changes may also occur. With modern advances in brain imaging technology, Computerized Tomography (CT) scan and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are the most commonly used diagnostic tools.
MRI does not involve radiation risk. Patients are required to lie inside the scanner with a strong magnetic field. Patients will not feel pain during the scanning process. MRI images can be achieved in a number of different angles and through a variety of different "signals", so as to letting us to explore more about the tumors’ nature, thus allowing neurosurgeons making the most appropriate treatment plan for patients.
Nowadays the microsurgery techniques allow neurosurgeons to perform minimally invasive brain surgery in a more secured environment. Under normal circumstances, patients often do not need to shave off bold for undergoing a brain surgery. Postoperative recovery time is also much shortened. For certain types of tumors, such as acoustic neuroma, non-surgical methods such as radiosurgery treatment is also available to be an effective and yet reliable treatment options carries only few side effects.